The Procedure
Sometimes also called labia minor reduction or labial reduction
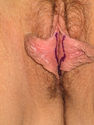
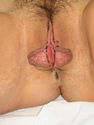
Labioplasty or labiaplasty is an operation which is designed to reduce and reshape the excess labia minora tissue of the vagina. Women seek surgery to this location for multiple reasons. Most women are concerned about the discomfort and also the appearance caused by labial elongation.
The symptoms which women normally describe being associated with the excess tissue include discomfort and pain with certain activities such as prolonged sitting, cycling and sexual intercourse (dyspareunia).
Labial reduction is usually carried out on the labia minora. These are regarded as the “inner” lips on either side of the entrance to the vagina. Many women also seek surgery to remove the excess labial tissue which may show in certain types of clothing, and to improve the general appearance of the genitalia. Some women live with this discomfort for many years and adopt various strategies to reduce discomfort such as wearing loose clothing. Many women only recently have become aware that something can actually be done to improve the situation.
Cosmetic concerns regarding the appearance of the labia may have been present since early teenage years. Labia minora elongation is a natural phenomenon which takes place over time and can be exacerbated by pregnancy and subsequent childbirth.
The changes that can occur to the labia include increase in length and diameter and also an increase in pigmentation making the labia appear darker and also more prominent with respect to the labia majora (outer lips).
Women will usually consult with Dr. Belt about their particular needs and goals for labioplasty. Consultation involves a detailed discussion and an external examination.
To assist the healing patients should cleanse with water and shave the area one day prior to surgery, removing all the pubic hair around the labia.
The surgery is performed under a general anaesthetic.
Surgery is usually performed as a day case. Numerous techniques are available including :a trim of the labia minora, a crescentic excision of skin on the internal part of the labia minora, or the use of a wedge and flap closure to close the wound.
Surgery involves the careful and conservative removal of excess tissue. The wound is closed using two layers of dissolving sutures, which do not require later removal.
The patient is then generally discharged home with strong oral painkillers and antibiotics for five days.
Some bruising may result from the procedure and patients are advised to have regular baths and apply a topical ointment.
It is generally recommended that ice is applied between two layers of underwear for the first twelve hours. After surgery most patients need to take a minimum of three to four days off work. This will allow for swift wound healing.
It is important to wear loose comfortable clothing after the surgery.
The patients must discuss the time scale of return to sporting and sexual activities with Dr. Belt prior to the surgery.
The main risks of labioplasty are wound infection and wound breakdown.
Post surgery patients should cleanse with water and avoid harsh chemicals and dry by simply dabbing the area rather than vigorous rubbing.
Labioplasty can improve the physical and physiological quality of life for many women.
Dr Belt has publications relating to labioplasty including a story from one of his patients featured in Marie Claire.
He has also written an article in Vogue and been interviewed on ABC radio regarding this procedure.
Dr Belt is an expert in labioplasty and has recently been on the National Medicare Benefit Schedule Review Committee assessing he use of labioplasty through Medicare in Australia.

Complications and Risks
All Procedures have potential complications and risks. These can be divided into general complications and those specific to each procedure. The latter are listed in the FAQs below.
General complications include:
- Wound complications - bleeding, bruising, collections under the skin of blood (haematoma), pus (abscess), serous fluid (seroma), infection, wound breakdown, suture extrusion, sensory loss;
- Aesthetic complications - poor scars, stretched scars, raised scars (keloid or hypertrophic), contour irregularities, need for revisional procedure;
- Anaesthetic complications
Downloads
FAQs
-
What are the costs involved?
Dr Belt’s fee, theatre fee, day bed and price of overnight accommodation (if not a day case), and the specialist anaesthetist fee.
Our fees attract rebates from Medicare and Health Funds, please contact Dr Belt’s rooms for a specific quote.
-
What are the potential risks?
These can be broken down into those general risks for any procedure and those specific to the procedure.
General risks include bruising, swelling, bleeding, wound infections, anaesthetic related problems and problems related to abnormal scarring (hypertrophic, keloid & stretched scar).
Specific risks include asymmetry, wound breakdown, collections of fluid underneath the skin and mucosa (lining tissue), including serum (seroma), blood (haematoma), pus (abcess), under or over resection of labial tissue and failure to improve the symptoms or apperanace. The clitoris is not touched and changes in sensation should not be experienced.
-
What happens after the surgery?
This surgery is usually performed as a day case. No drains are used. You will be allowed home after 4 hours and once you have passed urine. Ice should be applied to the area for the next 12 - 24 hours. Topical ointment is used for a week. You will be seen regularly at Day 7 and then 3, 6 & 12 months post operatively.
-
What type of anaesthetic is used?
Dr Belt’s preference is to perform surgery under a general anaesthetic. Dr Belt has performed the procedure, in certain circumstances, under a sedation and local anaesthetic. A consultant specialist anaesthetist administers the sedation.
Minor revisional procedures, if required, can be performed under local anaesthetic alone. Dr Belt’s revisional rate is 3%.